craigs test for torsion angle|craig's test hip : wholesale Angle measurement: Measure the angle of internal or external rotation using the goniometer. Interpretation: Normal: At birth, the mean . Resultado da r/Ontario_OnlyFans: This is a community for OnlyFans creators in Ontario Canada to meet, discuss, advertise, and creat more 🔥🔥🔥 content with each.
{plog:ftitle_list}
MINHAMOB. O SEU APP. 100% TURBINADO. Disponível no. Google Play. Disponível no. App Store. Emissão de 2ª via de boleto. Mudança de titularidade.
what is a craig's test
Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence . See more
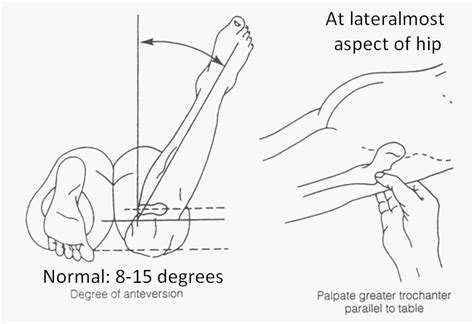
Angle measurement: Measure the angle of internal or external rotation using the goniometer. Interpretation: Normal: At birth, the mean . The degree of anteversion can be assessed by measuring the angle of internal rotation of the hip. 10-15 degrees of anterior torsion is normal. Relevant Research Diagnosis is made clinically with the presence of intoeing combined with an increase in internal rotation of the hip of greater than 70° with an accompanying decrease in external rotation of the hip of less than 20°. .
Oxygen Vapor Transmission Rate Test System trade
femoral anteversion angle test
Craig's Test. Purpose: To determine the anteversion of the femur. Test Position: Prone. Performing the Test: The tested limb's knee is placed in 90 degrees of flexion. The examiner rotates the hip medially and laterally, while palpating the .
The Craig's Test is used to determine if femoral anteversion (inward twisting of the femur) is present. Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equilibrium.In this case, the assumption is that when the trochanter is most lateral during the rotation of the femur, the femoral neck is parallel to the floor and the angle of the tibia will indicate the FNA. . This Technique Peek Series video features Benjamin Gelfand, DPT, SCS, demonstrating how to perform the Craig's test, which is used to assess for femoral ante.Using a goniometer with the stationery arm perpendicular to the floor (representative of the femoral neck axis) and the moving arm in line with the shaft of the tibia (representative of the .
Craig's Test is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess the angle of femoral anteversion or retroversion. Evaluate hip rotation, identify abnormalities in femoral alignment, and guide appropriate treatment for improved hip .
Download the FREE Physiotutors App 📲: https://www.physiotutors.com/physiotutors-app/ONLINE COURSES: https://study.physiotutors.comGET OUR ASSESSMENT BOOK ︎.Craig's Test: Examination type: Postural Assessment: . the therapist can determine the angle of torsion. The degree of anteversion can then be estimated, based on the lower leg's angle with the vertical. Positive Test: If . Craig's Test is a special examination technique that measures the femoral anteversion in patients presenting with knee pain or other symptoms. . Trochanteric prominence angle test; Purpose [] Demonstration of Craig's .
This video tutorial takes you through this important test for the Hip Joint! It teaches you the methodology, and how to interpret your findings!⭐ SITE: ht.Methods: Thirty-eight participants with chronic hip joint pain (CHJP) and 38 matched controls participated. MRI was used to determine FVMRI. A digital inclinometer was used to assess Craig’s test, hip internal rotation (IR) and external rotation (ER) with hip flexed to 90°(90°), and hip IR/ER with hip in neutral flexion/extension (0°). If you have a patient that has trouble walking, then administer the Craig’s Test to gauge their femurs for any signs of high femoral anteversion or retroversion and see if they are at risk of developing one or if it’s a sign of other complications they might have or are developing.
Oxygen Water Vapor Transmission Rate Test System trade
Craig's test is a passive test used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. The examiner palpates the greater trochanter and rotates the hip internally and .
The Craig’s test for high school baseball players is a predictor of HIF and HIE in the lead hip and trail hip. Because the Craig’s test results are the largest predictor of hip internal rotation, the soft tissues and femoral anteversion angle assessed by the Craig’s test need to be evaluated among baseball players.
Craig's Test Also Known as: the Ryder Method. Background: This test measures femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. Procedure: The patient lies prone with the knee flexed to 90 degrees. . based on the angle of the lower leg with the vertical. (Magee 2002) page revision: 0, last edited: 13 Sep 2008 00:02.
In this video, I explain and demonstrate Craig’s test, a special test used in the assessment of femoral anteversion and retroversion, mostly in the pediatric. The Craig’s test, internal and external rotation of the hip, the Ely test, Ober’s test, and FAA on the CT were assessed. [Results] The FAA on the Craig’s test and CT in female patients was 24.3 ± 3.9° and 23.0 ± 10.3°, respectively on the uninjured side and 25.0 ± 5.2° and 20.3 ± 11.2°, respectively on the injured side, indicating .Craig’s Test (Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test) can easily be performed without costly imaging and can help assess femoral/hip anatomy. To perform Craig’s Test, follow these steps: . The normal angle of torsion should fall between a window of 8-15 degrees of internal rotation (tibia shaft away from the midline). .The Craig’s test, internal and external rotation of the hip, the Ely test, Ober’s test, and FAA on the CT were assessed. . The amount of torsion corresponds to the angle of the flexed lower .
This Technique Peek Series video features Benjamin Gelfand, DPT, SCS, demonstrating how to perform the Craig's test, which is used to assess for femoral ante.Craig's Test does not provide highly valid values to reflect the true femoral anteversion despite its clinical significance. Greater femoral anteversion may be associated with increased static knee external rotation, possibly resulting in increased quadriceps-angle and .
Calibration was performed with the vertical line extending from the table during each Craig’s test, and the angle displacement between the vertical line and the end position was recorded. . The femoral torsion index (FTI) is another femoral anteversion measure. It is considered easier to find the femoral torsion. Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of . It is indicate to degree of torsion of the femur. This angle decreases during the growing period. . But No significant correlation is found between this angle of Craig’s test & CT measurements on both sides which is involved side – r=0.12, .
Craig’s test, and the angle displacement between the vertical line and the end position was recorded. In the third method, femoral anteversion was measured . The femoral torsion index (FTI) is another femoral antever-sion measure. It is considered easier to find the femoralHip rotation range of motion and Craig's test may be used to screen for femoral version abnormalities. . also known as the trochanteric prominence angle test (Ruwe et al., 1992; Sangeux et al., 2014), and hip rotation range of motion . Femoral neck torsion angle measurement by computed tomography. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1987; 11:799-803 .[Purpose] This study aimed to compare the Craig's test and computed tomography (CT) in measuring the femoral anteversion angle (FAA) in patients with anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries. The relationship between the FAA measured on CT, and the range of axial rotation of the hip joint and muscl .Stress-Relaxation Torsion Test: This test measures how torsional stress decreases over time at a constant strain, relevant in applications where long-term stress relaxation is a concern. Creep Torsion Test: In this method, a constant torsional load is applied for an extended period to observe how the material deforms over time, known as creep.
Also known as Craig’s test or trochanteric prominence angle test. Measures amount of femoral torsion. Craigs test can also be performed to roughly calculate femoral anteversion. To do this, find the point of rotation where the greater trochanter is most laterally positioned. . [Computed tomographic torsion-angle and length measurement of the lower extremity. The methods, normal values and radiation load]. RöFo (1992);157(3):245. Google Scholar
Der Craig’s Test (Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test, Ruwe’s Test) und die Hüftinnenrotation weisen auf eine klinisch relevante Validität und Reliabilität hin. Es wird empfohlen, mehrere .
The femoral anteversion test, traditionally known as Craig’s test, will give the examiner an idea of femoral anteversion and retroversion (Fig. 26b). Palpate the greater trochanter and internally/externally rotate the hip until the greater trochanter is in the most lateral position. Note the angle of the lower leg compared to vertical. Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test (TPAT)'. Femoral anteversion is the angle between the femoral neck and femoral shaft, indicating the degree of torsion of the femur. It is also known as Femoral neck anteversion.

craig's test hip
Materiais que atraem os olhares do consumidor. Sim, os ade.
craigs test for torsion angle|craig's test hip